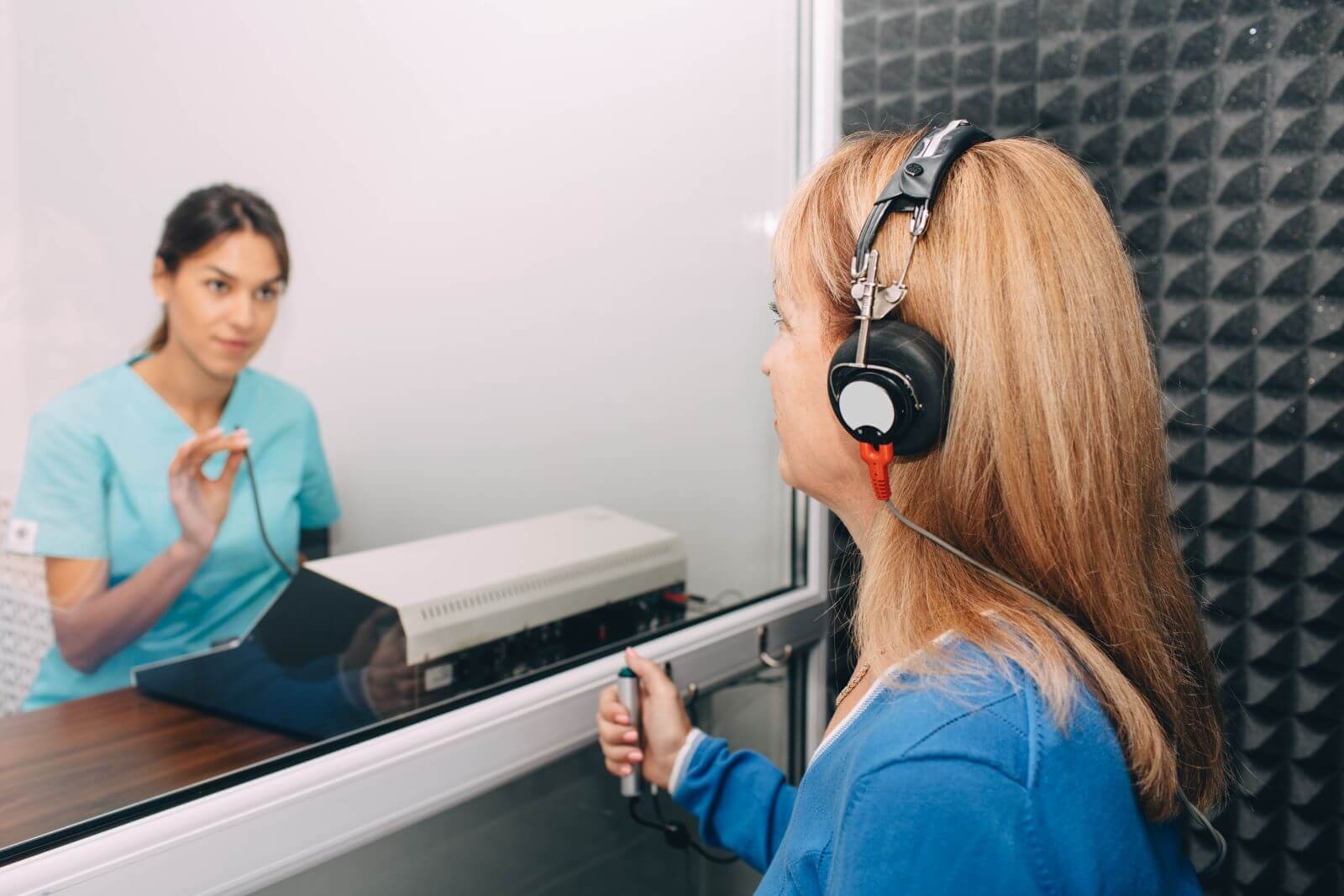
What to Expect at a Hearing Test
Hearing tests are an important step in determining if a person has hearing loss or some form of auditory disorder. It is also used to measure how well one can process and distinguish different sounds. Typically administered by professional audiologists, they will use the results of a hearing test to help diagnose hearing problems or check for ear infections.
Although there are five main stages or components, the majority of the testing process involves wearing headphones while situated in a soundproof space and responding to different tones and noises. Depending on the type of hearing test, it may evaluate one or both ears. A hearing test can often provide insight into overall hearing health, giving audiologists valuable information that helps them determine the best possible treatment options.
As each individual's hearing circumstances are different, not everyone will necessarily need to complete all five parts of the hearing exam. Nevertheless, understanding each stage allows for a smoother, more relaxed testing process as well as more accurate results. In general, the components of a comprehensive hearing test include:
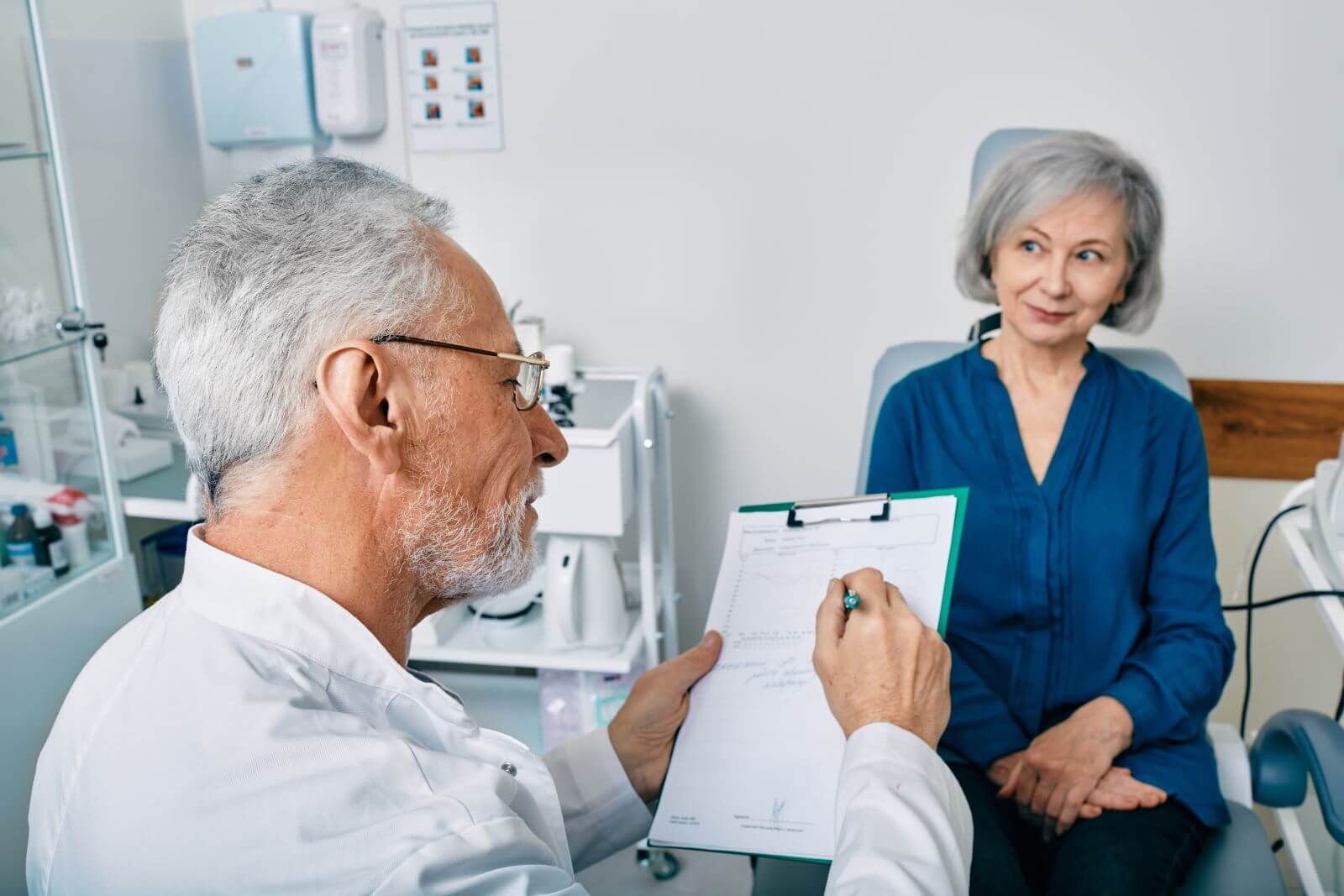

Medical History Review
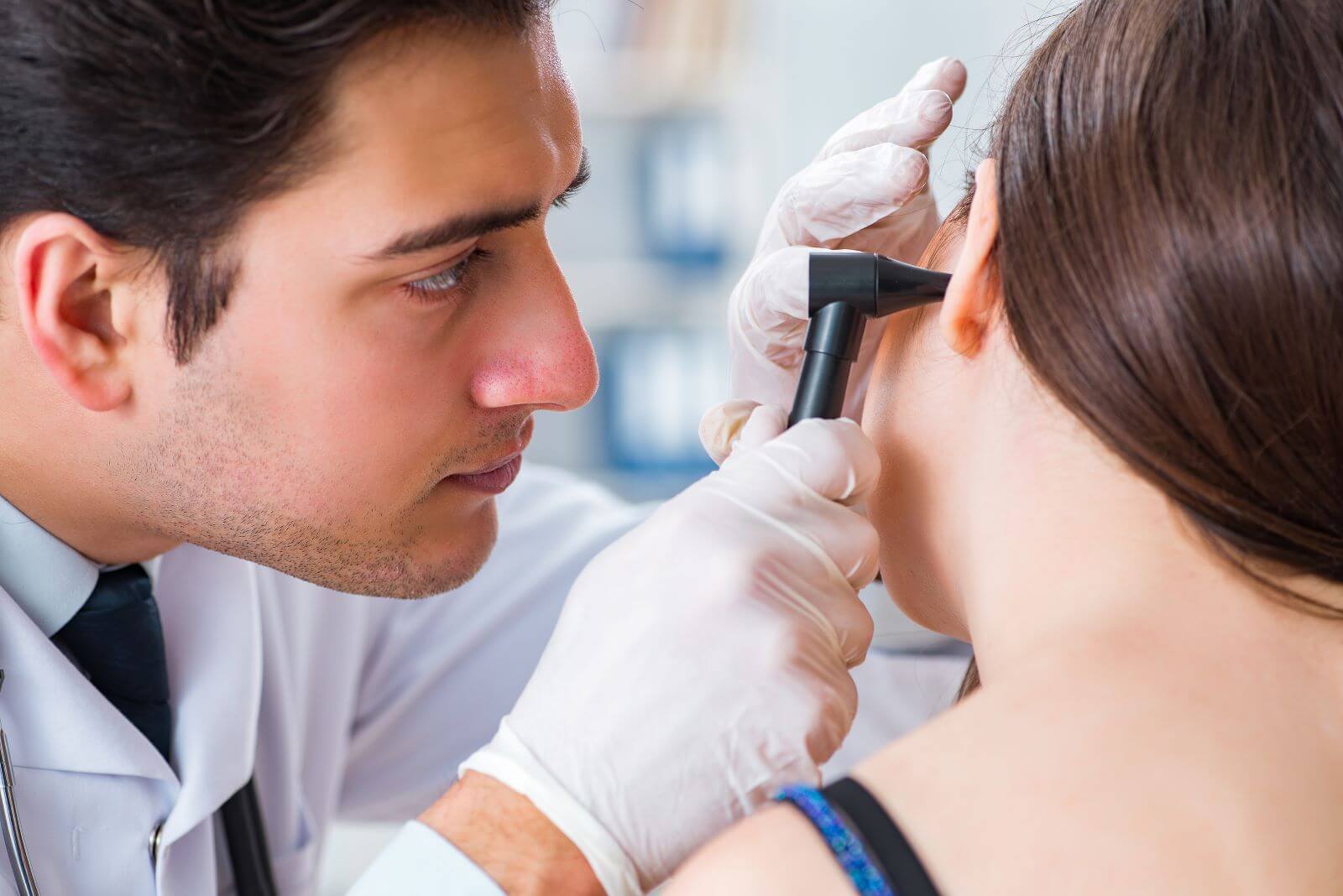
Otoscopy
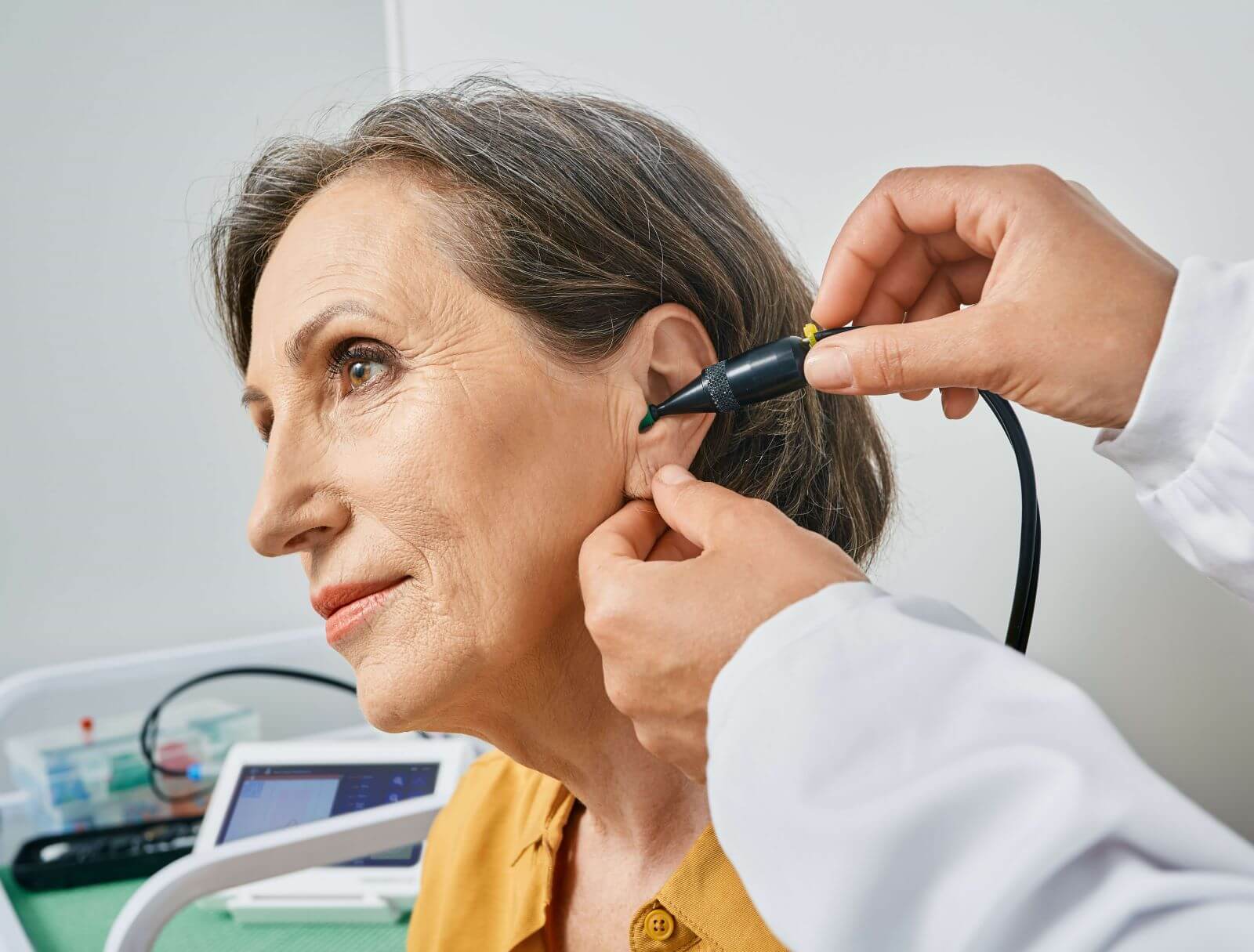
Tympanometry
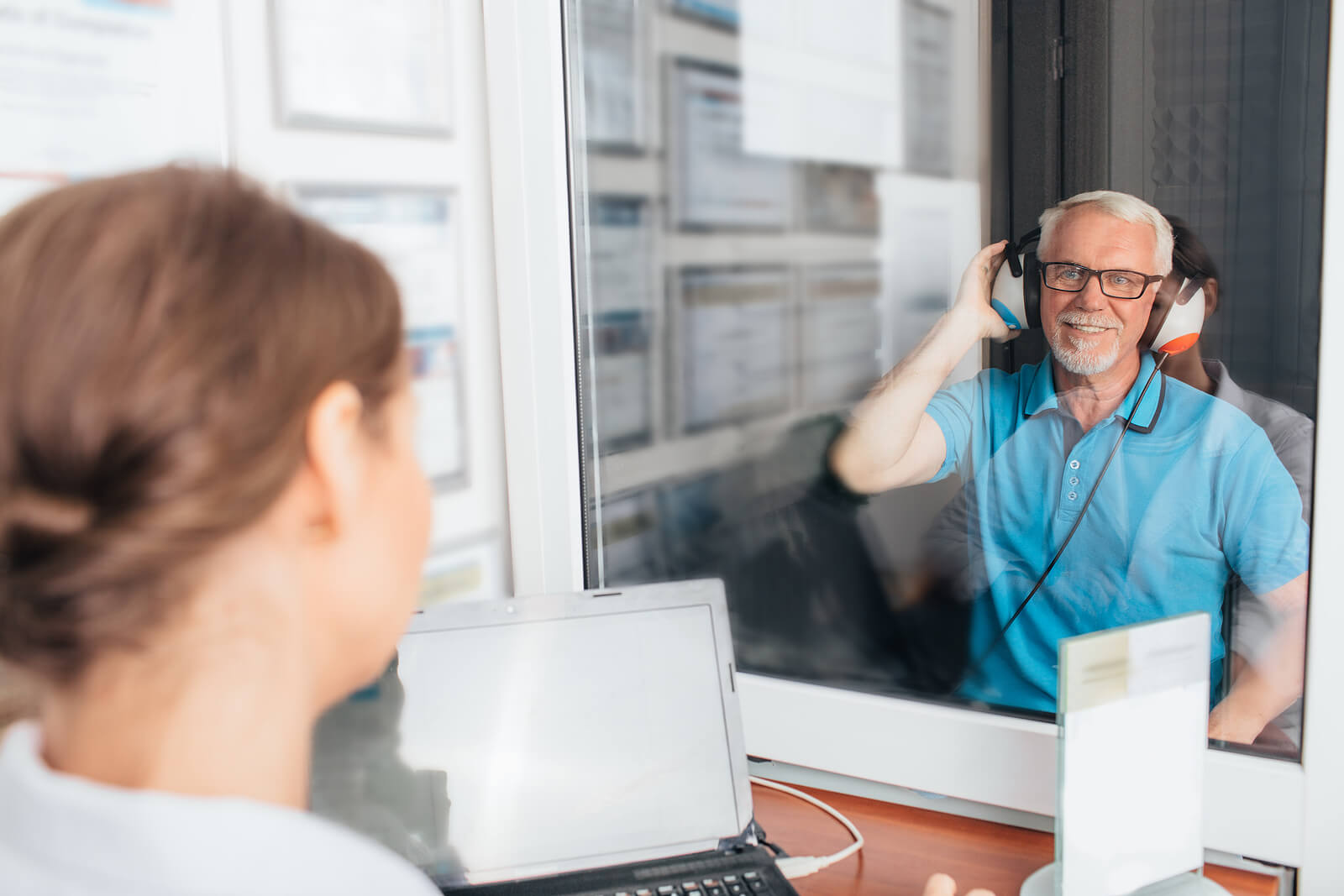

Speech Testing

